In modern workplaces, PowerPoint charts are no longer optional design elements. They are essential tools for communicating data, insights, and decisions. Whether you are presenting quarterly performance to stakeholders, explaining research results to students, or aligning cross functional teams around metrics, well designed charts can significantly improve understanding and engagement.
Effective PowerPoint chart creation is not just about making slides look good. It is about transforming raw data into visual stories that audiences can quickly interpret and act on. This guide explores practical PowerPoint chart techniques and methods, covering chart types, step by step creation workflows, and real world application scenarios. You will also learn how intelligent tools like Presenti AI can streamline chart creation and improve collaboration without sacrificing accuracy or clarity.
1. Understanding Common PowerPoint Chart Types
Choosing the right chart type is the foundation of effective data visualization. Each chart serves a specific purpose, and using the wrong one can obscure insights or confuse viewers.
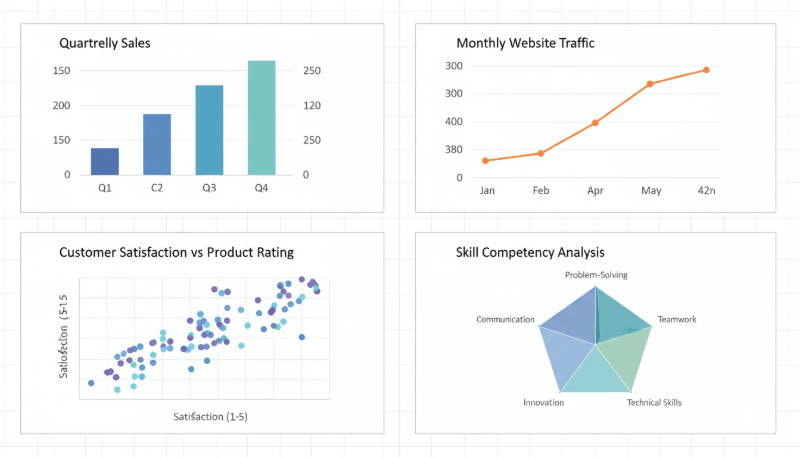
Column Charts and Bar Charts
Column and bar charts are ideal for comparing values across categories. They are widely used in business reporting, such as comparing quarterly revenue by department or feature adoption across customer segments.
- Best for side by side comparisons
- Easy to scan and understand
- Works well with labeled data points
Line Charts
Line charts are designed to show trends over time. They are commonly used in financial analysis, product growth tracking, and operational monitoring.
- Highlights increases or decreases
- Suitable for time series data
- Supports multiple data lines for comparison
Pie Charts
Pie charts show proportions and percentage breakdowns. While simple, they should be used carefully and only when the number of categories is limited.
- Best for showing parts of a whole
- Effective for budget allocation or market share
- Avoid using too many slices
Scatter Plots
Scatter plots reveal relationships or correlations between two variables. They are especially useful in analytics, experimentation, and performance analysis.
- Identifies patterns and outliers
- Supports trendlines and regression analysis
- Useful in marketing, finance, and data science contexts
Radar Charts
Radar charts are suitable for comparing multiple variables across a single subject or a small group. They are often used in performance evaluations and skill assessments.
- Displays multi dimensional data
- Helps identify strengths and weaknesses
- Best used with limited datasets
2. Step by Step PowerPoint Chart Creation Guide
When creating PowerPoint charts, clarity and simplicity should always guide your design decisions. With the help of AI powered tools like Presenti AI, you can reduce manual work and focus more on data accuracy and storytelling.
2.1 Inserting Charts into PowerPoint Slides
Start by opening your presentation and navigating to the slide where the chart is needed.
- Click the Insert menu in PowerPoint and select Chart
- Choose the appropriate chart type, such as column, line, or pie
- Enter or paste your data into the embedded data table
- Add clear axis labels and meaningful data point labels
Once the chart is added to the slide, Presenti AI can automatically adjust layout spacing based on the volume of data. This prevents charts from looking overcrowded or underutilized without requiring manual resizing.
2.2 Enhancing Chart Design and Sharing with Teams
A chart is only effective if it is visually readable and consistent with the rest of the presentation.
- Adjust colors, legends, and label positions to improve readability
- Double click the chart to update data or formatting quickly
- Maintain consistent color usage across all slides
Presenti AI offers predefined visual themes that align with common business and educational presentation styles. These presets help maintain visual consistency while saving time.
Collaboration is another critical factor. Presenti AI supports real time, multi user editing, allowing teams to work on charts and slides simultaneously. This is particularly useful for remote teams, project managers, and cross department presentations.
After finalizing your charts, presentations can be exported in formats such as PPTX or PDF. You can also share a presentation link, enabling viewers to access the content without downloading files.
3. Real World Applications of PowerPoint Charts
Understanding how to apply charts in real scenarios helps bridge the gap between theory and practice. Below are common use cases that reflect how professionals in North America and Europe typically use PowerPoint charts.
3.1 Sales Performance Analysis Using Column and Line Charts
Objective: Analyze sales performance across time periods to support planning and forecasting.
Chart Combination:
- Column charts display monthly or regional revenue
- Line charts show overall growth trends
Best Practices:
- Use dual Y-axes to display revenue and growth rate together
- Highlight peak sales periods with data labels
- Keep the focus on actionable metrics
This approach is commonly used by sales leaders and revenue operations teams to identify seasonality and adjust promotional strategies.
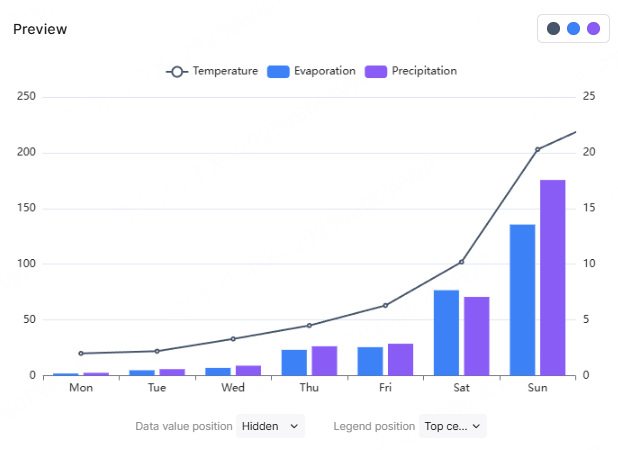
3.2 Market Research Reporting with Pie and Bar Charts
Objective: Present market share and customer preferences clearly for strategic decision making.
Chart Combination:
- Pie charts illustrate brand or product market share
- Bar charts compare preferences across demographic groups
Best Practices:
- Assign distinct, recognizable colors to pie segments
- Sort bar charts from highest to lowest values
- Limit the number of categories to maintain clarity
These techniques are frequently used in consulting reports, SaaS product analysis, and marketing strategy presentations.
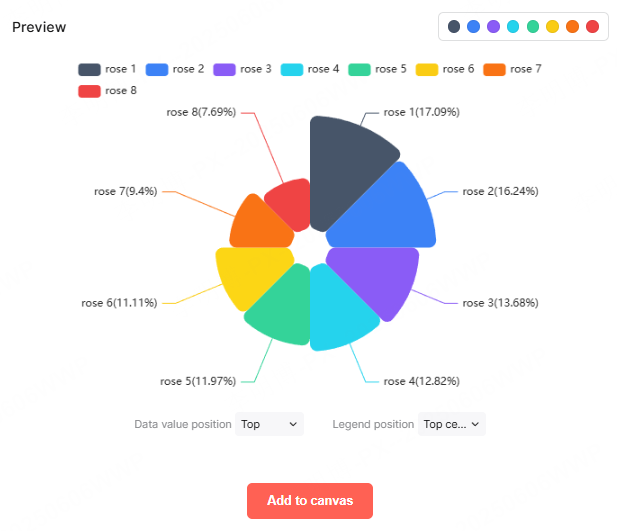
3.3 Educational Assessment with Scatter and Radar Charts
Objective: Evaluate student performance and competencies from multiple dimensions.
Chart Combination:
- Scatter plots show score distribution across exams or assignments
- Radar charts visualize skills such as analytical ability, collaboration, and engagement
Best Practices:
- Add trendlines to scatter plots to show overall performance direction
- Use color coded radar segments to identify strengths and gaps
Educators and academic administrators often use these visualizations to support data driven instruction and curriculum improvement.
4. Best Practices for Clear and Professional Data Visualization
Regardless of chart type or audience, several principles apply universally:
- Avoid unnecessary decorative elements
- Use concise titles that explain the insight, not just the data
- Ensure labels and legends are readable at presentation distance
- Align chart design with presentation goals
By combining these principles with intelligent automation, tools like Presenti AI allow professionals to focus on insights instead of formatting. Beyond chart creation, Presenti AI can generate complete, high-quality presentations, helping teams save time while maintaining a professional standard.
Conclusion
PowerPoint chart creation is both a technical and strategic skill. When done correctly, charts can turn complex datasets into clear narratives that drive understanding and decision making. By selecting appropriate chart types, following structured creation workflows, and applying real world use cases, you can significantly improve the effectiveness of your presentations.
With the added support of AI driven tools such as Presenti AI, creating professional, accurate, and visually consistent charts becomes faster and more collaborative. This allows you to spend less time on slide mechanics and more time delivering insights that matter.